|
The
Water Cycle
Water on Earth is always changing. Its repeating changes make a
cycle. As water goes through its cycle, it can be a solid (ice),
a liquid (water), or a gas (water vapor). Ice can change to become
water or water vapor. Water can change to become ice or water vapor.
Water vapor can change to become ice or water.
How do these changes
happen? Adding or subtracting heat makes the cycle work. If heat
is added to ice, it melts. If heat is added to water, it evaporates.
Evaporation turns liquid water into a gas called water vapor.
If heat is taken away
from water vapor, it condenses. Condensation turns water vapor into
a liquid. If heat is taken away from liquid water, it freezes to
become ice.
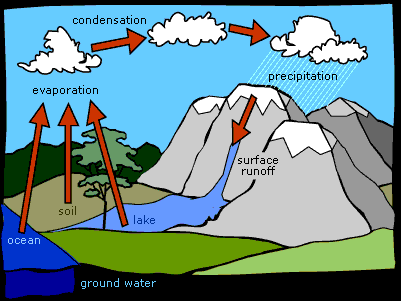
The water cycle is called
the hydrologic cycle. In the hydrologic cycle, water from oceans,
lakes, swamps, rivers, plants, and even you, can turn into water
vapor. Water vapor condenses into millions of tiny droplets that
form clouds. Clouds lose their water as rain or snow, which is called
precipitation. Precipitation is either absorbed into the ground
or runs off into rivers. Water that was absorbed into the ground
is taken up by plants. Plants lose water from their surfaces as
vapor back into the atmosphere. Water that runs off into rivers
flows into ponds, lakes, or oceans where it evaporates back into
the atmosphere.
The
cycle continues.
Back
|











