|
Deciduous
Forest
The mid-latitude
deciduous forest biome is located between the polar regions and
the tropics. Because of its location, air masses from both the cold
polar region and the warm tropical region contribute to the changes
of climate in this biome. Photo
© 2000-www.arttoday.com

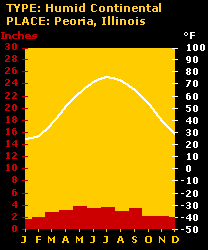
Mid-latitude
deciduous forests have both a warm and
a cold season (see climograph). Precipitation
ranges from 30 to 60 inches and is evenly
distributed throughout the year. Much
of the human population lives in this
biome. Although evergreens are found in
this biome, this biome is characterized
by an abundance of deciduous trees.
"Deciduous" means to
fall off, or shed, seasonally. Just as the name implies, these deciduous
trees shed their leaves each fall. Lying on the forest floor, the
leaves decay. As the leaves decompose, the nutrients contained in
the leaves are absorbed by the soil. For this reason, the soils
of this biome tend to be very fertile. Because this biome has fertile
soil and a long, 5 to 6 month, growing season, many deciduous forests
have been converted into agricultural regions.
Back
| Next
|











