Situation
 The habitat of the Florida Panther, which once ranged throughout the southeastern United States, has been in steady decline. Currently, the Florida Panther seeks shelter within the Florida Everglades. Today only
50 to 70 adult panthers remain in southwest Florida. They are among the most endangered animals in the world.
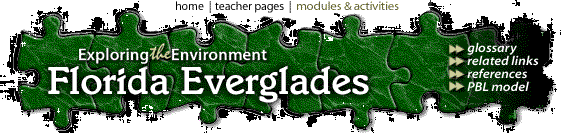
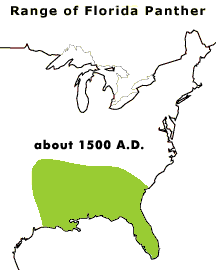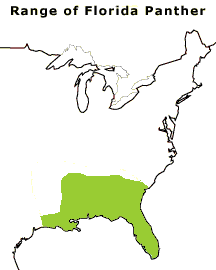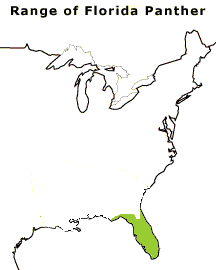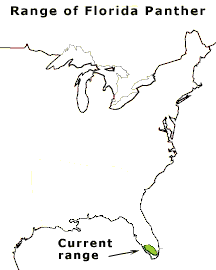
Image: Change in the range of the Florida Panther from 1500 A.D. to the present. Graphic courtesy
of Florida Panther Net, Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation
Commission.
The habitat of the Florida Panther, which once ranged throughout the southeastern United States, has been in steady decline. Currently, the Florida Panther seeks shelter within the Florida Everglades. Today only
50 to 70 adult panthers remain in southwest Florida. They are among the most endangered animals in the world.
Image: Change in the range of the Florida Panther from 1500 A.D. to the present. Graphic courtesy
of Florida Panther Net, Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation
Commission.
During the last century, settlement and farming in South Florida have dramatically altered the character of the historic Everglades.
It is half its original size. Its water supply has been diverted and controlled for uses like crop irrigation, city water supplies, and flood control.
 Over
the past few decades, people have begun to notice the negative environmental impacts caused by removing the water from the
Everglades' ecosystem. Private and government agencies have begun to fight for the protection of the Everglades, and people are taking an interest in preserving and restoring this unique wetlands ecosystem. In 1989, the "Modified Water Deliveries to Everglades National Park"
(Mod Waters) project was authorized by the Everglades National Park Expansion and Protection Act of 1989. This
act sanctioned the restoration of the natural cycle of water flow and level through the Florida Everglades. In 1994, the Everglades Forever Act was
passed. It provides for a comprehensive clean-up and restoration plan that
addresses problems with the quality, quantity, and timing of restored water flow and level.
Photo: A flood control structure in southern Florida. Photo courtesy of Robert Myers.
Over
the past few decades, people have begun to notice the negative environmental impacts caused by removing the water from the
Everglades' ecosystem. Private and government agencies have begun to fight for the protection of the Everglades, and people are taking an interest in preserving and restoring this unique wetlands ecosystem. In 1989, the "Modified Water Deliveries to Everglades National Park"
(Mod Waters) project was authorized by the Everglades National Park Expansion and Protection Act of 1989. This
act sanctioned the restoration of the natural cycle of water flow and level through the Florida Everglades. In 1994, the Everglades Forever Act was
passed. It provides for a comprehensive clean-up and restoration plan that
addresses problems with the quality, quantity, and timing of restored water flow and level.
Photo: A flood control structure in southern Florida. Photo courtesy of Robert Myers.
 However, preserving and restoring the Florida Everglades may not be as simple as opening a floodgate or pumping water back into the area.
Restoring the flow of water to these wetlands has had both positive and
negative consequences. Several complicated issues have caused controversy.
For instance, the Everglades Wildlife Refuge is worried that the restoration of the natural flow and level of water through the Everglades could
further endanger the Florida Panther. The Everglades Wildlife Refuge has asked
you to help them address their concern for the Florida Panther. You are
being asked to perform an Earth System Science (ESS) analysis of the
impacts of the restoration of water level and flow to the lithosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and atmosphere of the Everglades' ecosystem.
From this, you will make predictions about the future of the Florida Panther based on your ESS analysis.
Photo: Florida panther.
Photo
©
Larry Richardson, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
However, preserving and restoring the Florida Everglades may not be as simple as opening a floodgate or pumping water back into the area.
Restoring the flow of water to these wetlands has had both positive and
negative consequences. Several complicated issues have caused controversy.
For instance, the Everglades Wildlife Refuge is worried that the restoration of the natural flow and level of water through the Everglades could
further endanger the Florida Panther. The Everglades Wildlife Refuge has asked
you to help them address their concern for the Florida Panther. You are
being asked to perform an Earth System Science (ESS) analysis of the
impacts of the restoration of water level and flow to the lithosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and atmosphere of the Everglades' ecosystem.
From this, you will make predictions about the future of the Florida Panther based on your ESS analysis.
Photo: Florida panther.
Photo
©
Larry Richardson, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
ESS Protocol
First, you will do an
Earth system science analysis. Then, you will make predictions, based on
the results of the ESS analysis, concerning the future of the Florida
Panther.
Following the steps below will help you to accomplish your task for the Everglades Wildlife Refuge.
Step 2 -- List what is needed.
Step 3 -- Gather information to complete an ESS analysis.
Part I Event
Sphere
Part II Sphere
Sphere
Step
4 -- Present your findings.
Glossary ..|.. Related Links ..|.. References |..PBL Model
Home ..|.. Teacher Pages ..|.. Modules & Activities
HTML code by Chris
Kreger
Maintained by ETE Team
Last updated
April 28, 2005
Some images © 2004 www.clipart.com
Privacy Statement and Copyright © 1997-2004 by Wheeling Jesuit University/NASA-supported Classroom of the Future. All rights reserved.
Center for Educational Technologies, Circuit Board/Apple graphic logo, and COTF Classroom of the Future logo are registered trademarks of Wheeling Jesuit University.
